PM Narendra Modi Set to Unveil 5G Services in India, Social Media Boomed With Audience Happiness With 26.3K Digital Engagement
Revealing 5G ambitions of the country, Prime Minister Narendra Modi is set to launch 5G connectivity in India during a four-day launching event starting on the 1st of Oct. Essential telecom firms such as Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, and Vodafone-Idea will be initiating 5G technology in the country during the India Mobile Congress event.
CheckBrand noted the influence of 'PM Narendra Modi's launching 5G' in the digital arenas. According to the study, the unveiling event had 26.3K digital engagements from the internet audience. Apart from that, people have 14.7% of positive sentiments today; while 0.7% have negative thoughts. In the digital realm, it has a search engine score of 707.
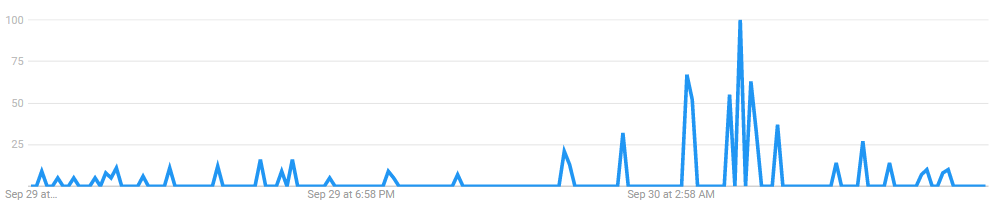
*Source: Google Trends
People stated on social media platforms about the event; a month after a Union minister instructed all telecom service providers to prepare for the service's roll-out.
Reliance Jio, India's largest carrier, intends to launch Jio 5G by Diwali 2022 across various significant cities, including the multicultural metropolises of Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai. The news comes about a month after Reliance Industries Ltd announced a 2 lakh crore investment to bring out 5G services in important cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata by Diwali, and across India by December next year 2023.
The India Mobile Congress
The India Mobile Congress (IMC), according to its official website, is Asia's largest telecom, media, and technology gathering, co-organized by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) and the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI).
As the 5G service is expected to be 10 times faster than its predecessor, with peak data transfer speeds of up to 20 GB per second or more than 100 MB per second, it opens up significant business opportunities in a variety of fields ranging from gaming to real-time surgery to driverless cars.
Indira Gandhi International Airport in Delhi is now India's first 5G-ready airport. According to DIAL, the airport operator, "passengers will be able to experience 20 times quicker speed compared to accessible Wi-Fi networks."

"We will deploy Jio 5G across numerous significant cities, including the metropolises of Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai, within the next two months, by Diwali." We will provide Jio 5G to every town, taluka, and tehsil in our country by December 2023, which is less than 18 months from today," Ambani said during the company's annual general meeting on August 29.
Leading Telecommunication Services in India
In contrast, Reliance's competitor, Bharti Airtel, promises to provide 5G services in 5,000 cities and towns by March 2024. In addition, Ambani's acquisitions helped the government earn a record 1.5 lakh crores by selling 51,236MHz of spectrum in a week-long auction. Consequently, Ambani's Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd emerged as the top buyer in the government auction of airwaves, paying 88,078 crore, more than twice that of second-placed Bharti Airtel Ltd.
Wireless operators purchased 71% of the 72,098MHz airwaves available for sale by the government, including 5G spectrum, with the biggest amount ($80,590 crore) coming from the sale of spectrum in the 3.3GHz band. The sale of airwaves in the 700MHz, 26GHz, and 1,800MHz bands provided respectively 39,270 crores, 14,709 crores, and 10,376 crores.
An Analysis of 5G Services in India
The 5th Generation of Information Technology: 5G
5G technology is the fifth generation of mobile networking technology. The levels of development, it has become now the new worldwide wireless standard. It provides a new type of network capability of connecting nearly everyone and everything, including machines, objects, and gadgets. Internet speed in the 5G spectrum has been tested to reach up to 20 Gbps while the greatest internet data speed in 4G has been reported at 1 Gbps in most circumstances.

The 5G network will not require any form of tower, but rather will transmit signals via tiny cell sites on roofs or power poles. Because of the millimetre-wave spectrum these tiny cells are much more relevant. Various cutting-edge 5 G technologies, including as MIMO and TDD will be deployed. Multiple Inputs and Multiple Outputs (MIMO) technology at the same time will enable downloading speed in GBs.
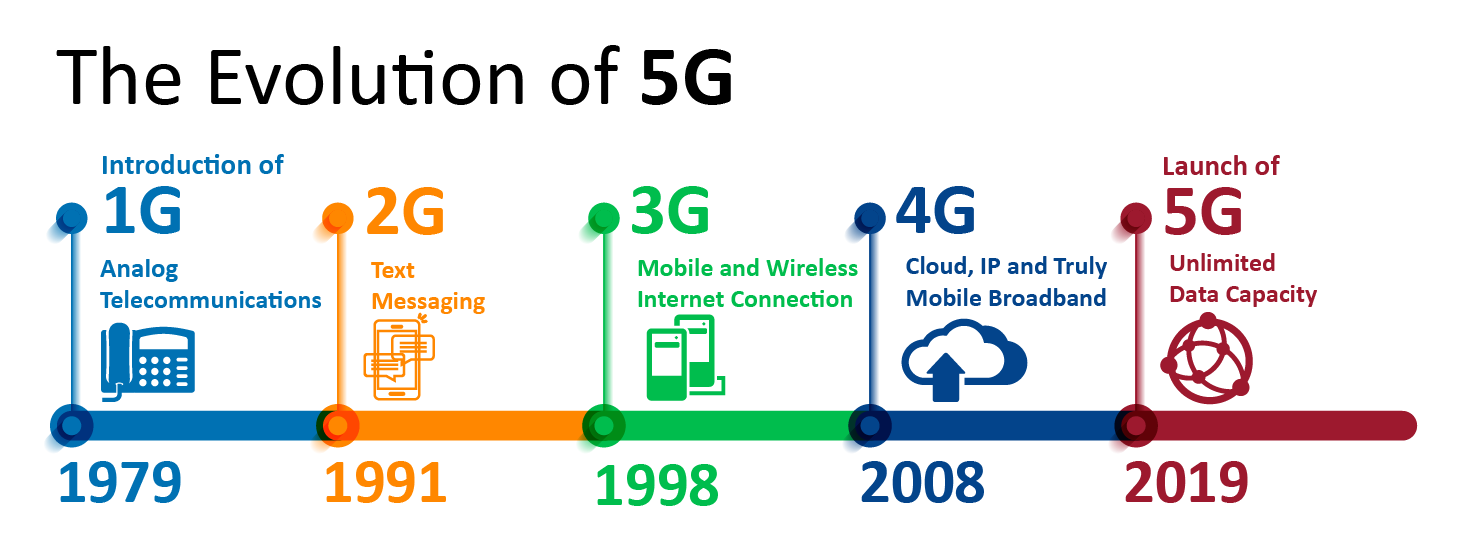
The Transition from the First to the Fifth Generation
1G was introduced in the 1980s and used analogue radio signals to handle solely voice conversations.
2G, employing digital radio signals and provides both speech and data transmission with a bandwidth of 64 Kbps, was introduced in the 1990s.
3G was introduced in the 2000s with speeds ranging from 1 Mbps to 2 Mbps and the capacity to send telephone signals such as digitised voice, video calls, and conferencing.
4G was introduced in 2009, with peak speeds ranging from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps, and it also supports 3D virtual reality.
Various Bands of 5G
5G primarily operates in three bands, namely low, mid, and high frequency spectrum — each of which has its own set of applications and restrictions.
Low Band Spectrum: The maximum speed of Internet and data exchange is restricted to 100 Mbps in terms of coverage and speed (Megabits per second). This means that telecom providers can utilise and deploy it for business mobile users who may not have high-speed Internet requirements. However, the low band spectrum may not be ideal for the industry's specialised demands.
Mid Band Spectrum: Having better speeds than low band but has high restrictions in terms of coverage area and signal penetration. This band might be utilised by companies and specialised production units to create captive networks that can be tailored to the demands of that industry.
High Band Spectrum: The fastest of the three bands, but with highly restricted coverage and signal penetration power. This band significantly improves future 5G technology applications such as Internet of Things (IoT) and smart technologies, although it will necessitate significant infrastructure.
Scope of Usage of 5G
In general, 5G is employed in three sorts of linked services: improved mobile broadband, mission-critical communications, and enormous IoT.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband: 5G mobile technology has the ability to provide new immersive experiences such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) with faster-more, consistent data-rates, reduced-latency, and cheaper cost-per-bit, in addition to enhancing our smartphones.
Mission-Key Communications: With ultra-reliable, available, low-latency communications like remote control of critical infrastructure, cars, and medical procedures, 5G can allow new services that can alter industries.
Large Internet of Things: 5G is designed to seamlessly link a massive number of embedded sensors in nearly everything by scaling down data speeds, power, and mobility—providing incredibly lean and low-cost connectivity.
Massive Internet of Things: When combined with IoT, cloud, big data, AI, and edge computing, 5G has the potential to be a crucial facilitator of the fourth industrial revolution.
Existence of 5G Technology Globally
The whole world is tremendously interested in 5G technologies and has been working very so fast to accomplish that. For the 50 bands, Japan has announced bands as high as 3700 MHz, 4500 MHz, and 28 GHz frequencies. Preliminary work on 50 European connections centred on a frequency band of about 3400 to 3800 MHz frequencies.
The United States of America is likewise making great advances in this sector. Along with this, nations like Ireland, the Czech Republic, South Korea, The United Kingdom, and other countries have completed the auction procedure for their 5G spectrum bands. For 5G connections, China's Industry & IT Ministry has specified frequency bands of up to 3300-3600 MHz, 3400-3600 MHz, and 4800-5000 MHz frequencies.
5G's Potential Benefits in India
India suffered a lot of delays in launching 2G, 3G, and 4G, but this time the government does not want to repeat the error of the past, and instead has set a target of commercially adopting 5G technology across the country by the end of 2020.
In India, a 5G technology committee was created, and its recommendations included the initial allotment of spectrum for 5G technology, increasing the quantity of available spectrum, and lowering spectrum prices. Simultaneously, it began efforts in three ways: arranging global conferences by India, organising national 5G events, and suggesting programmes for India's specialised 5G uses.

If 5G technology is successfully implemented in India, this will mark a revolution in the telecommunication sector of India. 5G technology in India can make the Bharat-Net project of the Government of India successful. Under the Bharat-Net project, the target is to provide a broadband facility of about 2 Mbps to 20 Mbps to all households. It is estimated that the digital economy will be encouraged by 5G technology in India, which will help India to become a 5 trillion dollar economy by 2024.
India's 5G Rollout Faces Difficulties
Low Fiberization Footprint: There is a need to enhance fibre connection throughout India, which now connects just 30% of telecom towers. This figure has to be doubled for an effective 5G India launch and uptake.
'Make in India' Hardware Challenge: The restriction on some foreign telecom OEMs (original equipment manufacturers), on which the majority of 5G technology development is based, is a significant barrier in and of itself.
High Spectrum Pricing: The cost of 5G spectrum in India is several times higher than the worldwide average. This will be bad news for India's cash-strapped carriers.
Choosing the Most Appropriate 5G Technology Standard:
To speed up the implementation of 5G technology the debate between the local 5G standard and the global 3GPP standard must be settled. While 5G offers obvious benefits, it also boosts the cost of 5G India implementation and poses compatibility problems for telecommunications.
Way Forward
Boosting Domestic 5G Production: If the government wants to realise the 5G India goals, it must stimulate and increase domestic 5G hardware manufacture at an unprecedented rate.
Pricing Rationalization: This spectrum pricing must be rationalised in order for the government to obtain appropriate income from the auction without jeopardising India's 5G development plans.
Bridging the Rural-Urban Gap:
5G can be installed at several band ranges with the low bands having a significantly greater range that is beneficial to rural regions.
|
About Us: CheckBrand is an AI-enabled platform that tracks your online presence, to analyse the digital ranking, brand value and popularity index. Our Digital Ranking analysis is based on five factors; (1) Followers, (2) Trends, (3) Engagement, (4) Sentiment and (5) Mentions. |
CATEGORIES
- Digital Marketing
- Marketing
- Entertainment
- Medical
- Science and Technology
- Politics
- Sports
- Environment
- Campaign
- Interview
- Viral
- What's Trending
- Trending News
- Viral Videos
- Youtube Trends
- Social Media Ranking
- Twitter Trends
- Google Trends
- Top Politicians
- Top Cricketers
- Top Influencers
- Best Campaigns
- Google News
- News
-
 Oct 11, 2020
Oct 11, 2020SEO Content Writing Vs. SEO Copywriting:...
-
 Dec 15, 2020
Dec 15, 2020#Karnatakaiphoneplantagitation: Workers...
-
 Dec 15, 2020
Dec 15, 2020#OLA Invests ₹2400 Crores For Our Futur...
-
 Dec 15, 2020
Dec 15, 2020#Snapchat Launches Astrology Profile
-
 Dec 15, 2020
Dec 15, 2020Know Why #BOYCOTTJIOSIM Is Trending On S...
-
 Aug 01, 2023
Aug 01, 2023India's Chandrayaan-3 On Track For Lunar...
-
 May 17, 2023
May 17, 2023Zara Hatke Zara Bachke Trailer Review(Ra...
-
 Aug 04, 2022
Aug 04, 2022'Har Ghar Tiranga' Campaign Created Stor...
-
 Dec 16, 2020
Dec 16, 2020#Skillhaitohfuturehai: Mahindra's Flagsh...
-
 Dec 15, 2020
Dec 15, 2020#OLA Invests ₹2400 Crores For Our Futur...
HIGHLIGHTS
- Realme Pad Specifications Teased, Will C...
- MARKETS: Sensex Down 300 Pts, At Days Lo...
- Afghanistan Crisis Live Updates: NIA Chi...
- Women Will Be Admitted To NDA, "Historic...
- Taliban's New Education Minister Says Ph...
- India's T20 World Cup Selection Question...
- New JioFiber Quarterly Broadband Plans I...
- Explained: How Your Cat Got Its Stripes...
- Who Is Aesha Mukherji? All You Need To K...
- Long Live Test Cricket While We've Virat...











